« Jellyfin » : différence entre les versions
| (14 versions intermédiaires par le même utilisateur non affichées) | |||
| Ligne 9 : | Ligne 9 : | ||
# apt install jellyfin | # apt install jellyfin | ||
On peut sur rendre sur <nowiki>http://</nowiki><font color = blue>IP_SERVEUR</font>:8096 pour vérifier le fonctionnement du service et faire la première configuration. | On peut sur rendre sur <nowiki>http://</nowiki><font color = blue>IP_SERVEUR</font>:8096 pour vérifier le fonctionnement du service et faire la première configuration. | ||
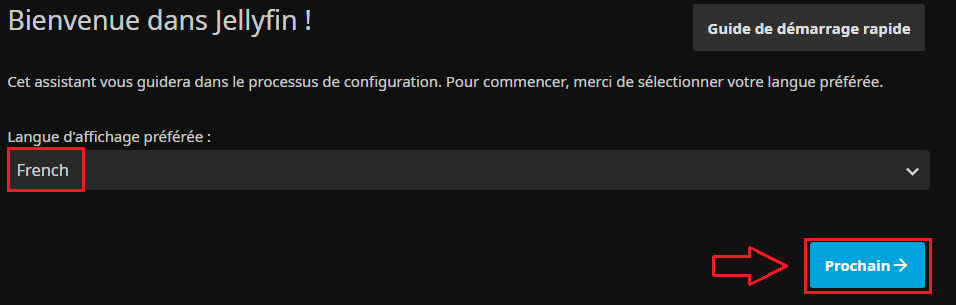
* On commence par le choix du langage préféré : | |||
[[Fichier:Jellyfin Install1.PNG|border|langage préféré..]] | |||
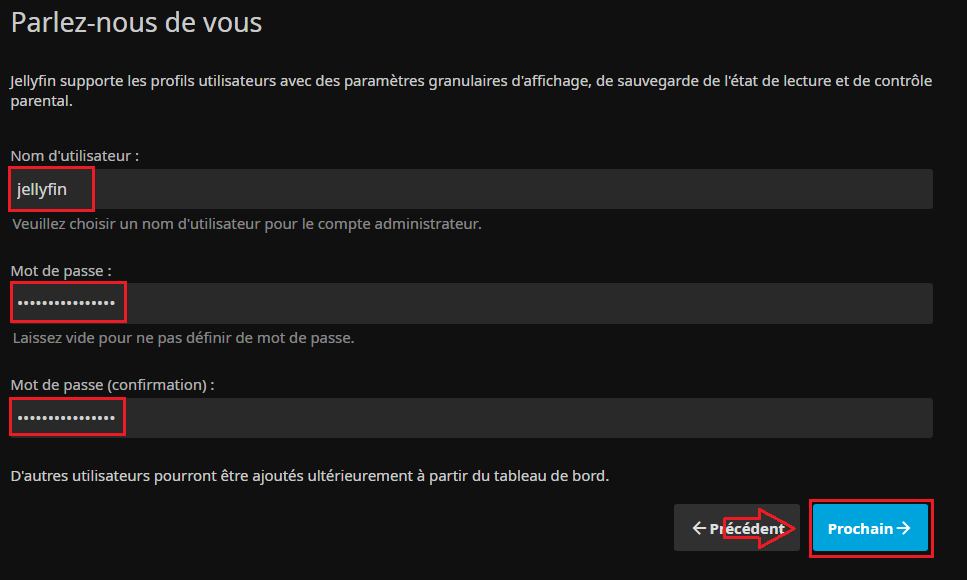
* On configure le compte d'administration et son mot de passe : | |||
[[Fichier:Jellyfin Install2.PNG|border|Configuration du compte d'administration..]] | |||
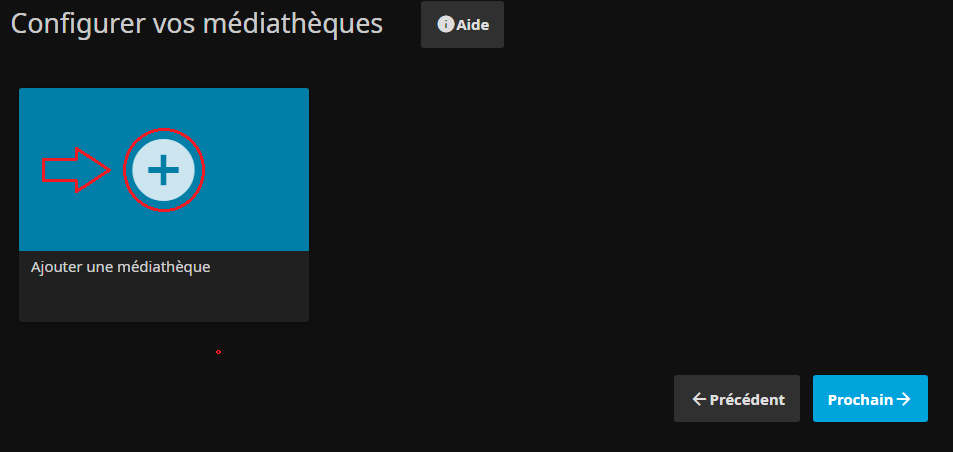
* On peut optionnelement inscrire tout de suite une ou plusieurs bibliothèques : | |||
[[Fichier:Jellyfin Install3a.PNG|border|Bibliothèque optionnelement..]] | |||
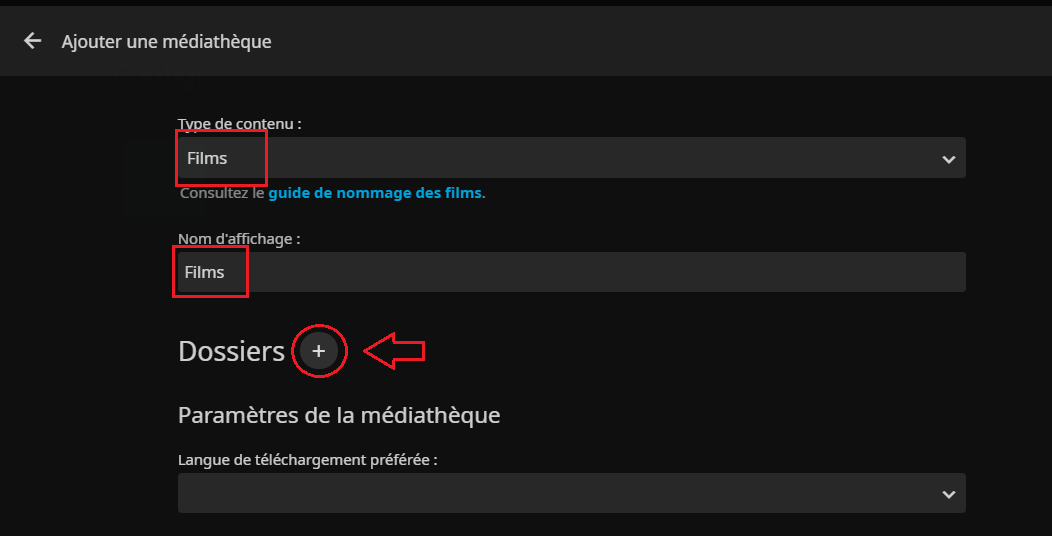
* Si l'on choisit d'ajouter une bibliothèque, on commence par choisir le type de médias et le nom, puis on choisit de configurer son emplacement : | |||
[[Fichier:Jellyfin Install3b.PNG|border|Options de bibliothèque..]] | |||
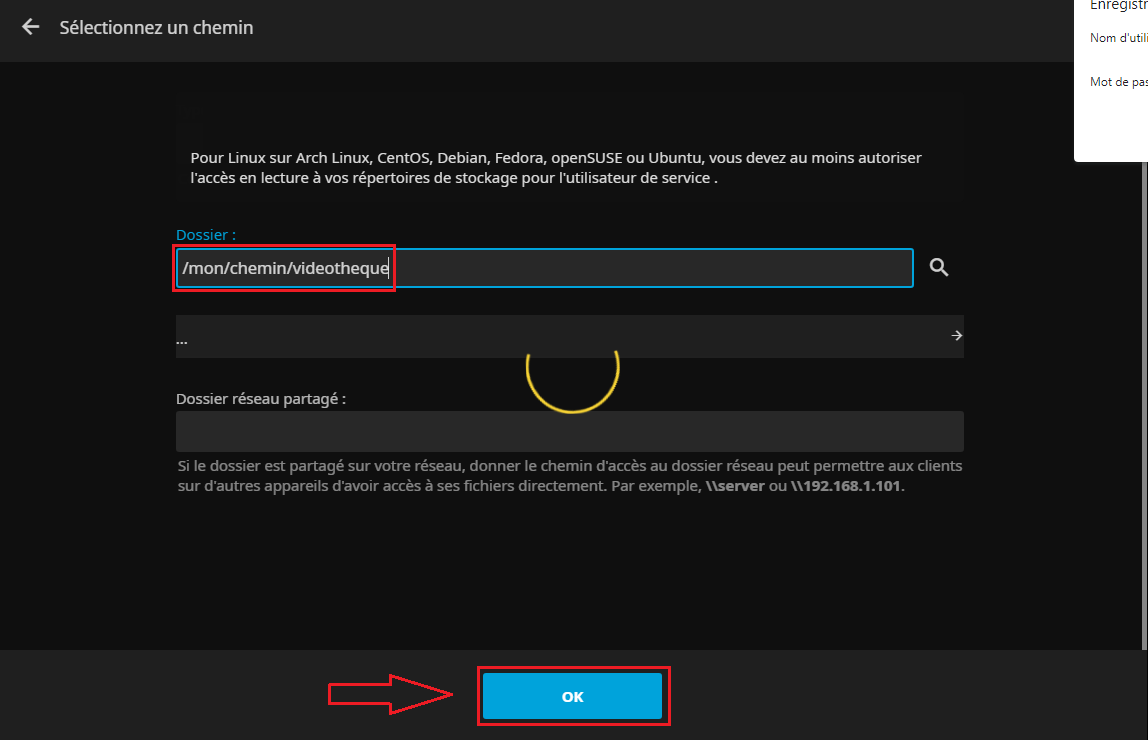
* On indique le chemin d'accès du dossier et on valide : | |||
[[Fichier:Jellyfin Install3c.PNG|border|C'est par ici..]] | |||
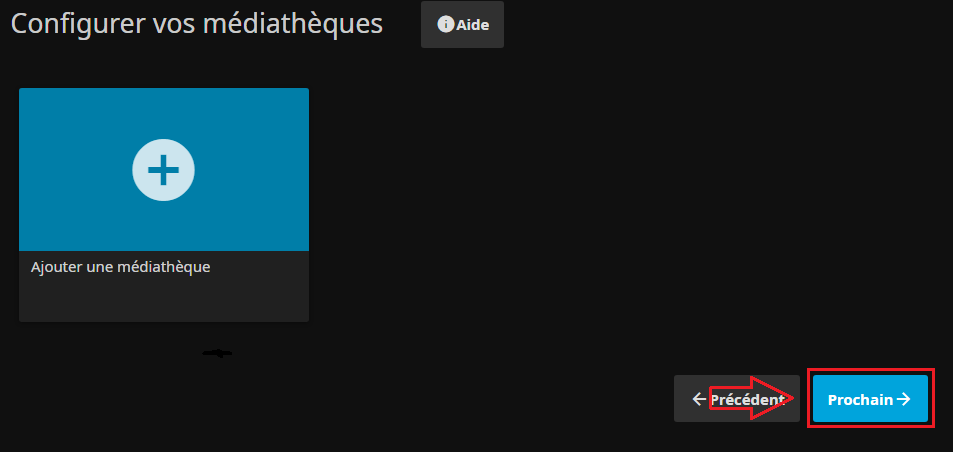
* Une fois la/les bibliothèques configurées ou laissées pour plus tard on pass à l'étape suivante : | |||
[[Fichier:Jellyfin Install3d.PNG|border|On peut continuer..]] | |||
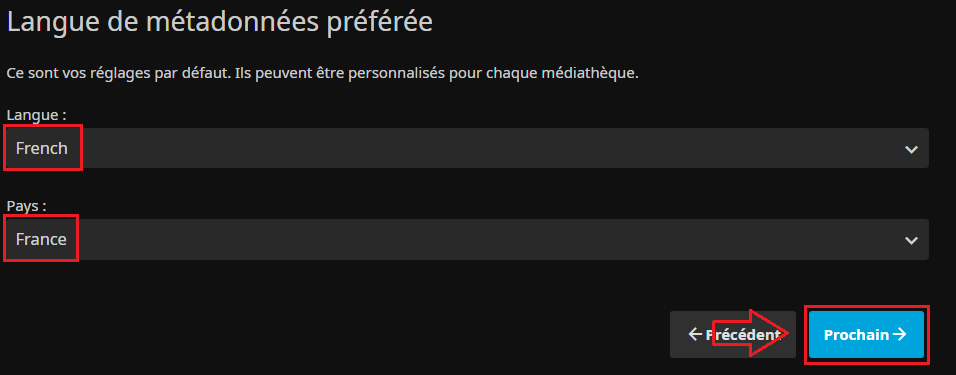
* Choix du langage par défaut pour les métadonnées : | |||
[[Fichier:Jellyfin Install4.PNG|border|Oui on préfère aussi le français pour les méta..]] | |||
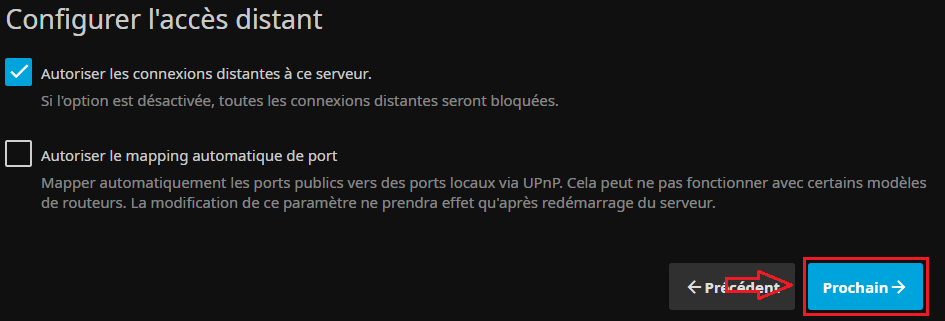
* On configure l'accès distant (a priori par défaut) : | |||
[[Fichier:Jellyfin Install5.PNG|border|Rien à signaler..]] | |||
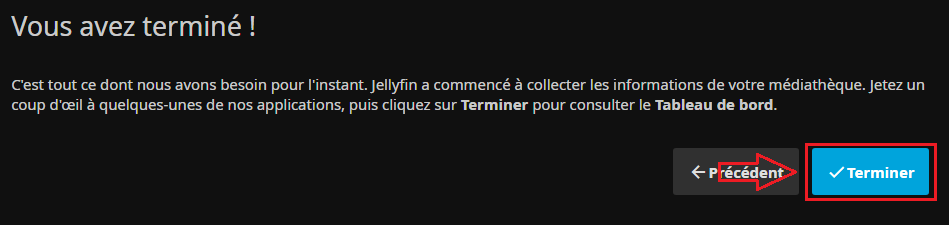
* Le serveur nous indique que la configuration de base est terminé : | |||
[[Fichier:Jellyfin Install6.PNG|border|C'était rapide !]] | |||
* On est redirigé sur l'écran d'accueil : | |||
[[Fichier:Jellyfin Install7.PNG|border|Bienvenue sur votre nouveau serveur de "streaming" :)]] | |||
==Sécurisation de jellyfin== | ==Sécurisation de jellyfin== | ||
{{Méta bandeau | |||
| niveau = modéré | |||
| icône = important | |||
| texte = Forcer le HTTPS au niveau de Jellyfin rend le service DLNA inutilisable. Il est recommandé de préférer l'utilisation d'un [[Nginx_ReverseProxy_LXC_Alpine_Linux|reverse-proxy]]. | |||
}} | |||
On crée le certificat : | On crée le certificat : | ||
# openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout /etc/jellyfin/jellyfin.key -out /etc/jellyfin/jellyfin.crt -nodes -subj '/CN=localhost' | # openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout /etc/jellyfin/jellyfin.key -out /etc/jellyfin/jellyfin.crt -nodes -subj '/CN=localhost' | ||
| Ligne 36 : | Ligne 62 : | ||
Maintenant l'interface de Jellyfin sera accéssible via <nowiki>https://</nowiki><font color = blue>IP_SERVEUR</font>:8920 | Maintenant l'interface de Jellyfin sera accéssible via <nowiki>https://</nowiki><font color = blue>IP_SERVEUR</font>:8920 | ||
== Vhost pour Reverse-Proxy == | |||
server { | |||
listen 80; | |||
listen [::]:80; | |||
server_name <font color = blue>jellyfin.exemple.net</font>; | |||
# Uncomment to redirect HTTP to HTTPS | |||
return 301 <nowiki>https://</nowiki>$host$request_uri; | |||
} | |||
server { | |||
listen 443 ssl http2; | |||
listen [::]:443 ssl http2; | |||
server_name <font color = blue>jellyfin.exemple.net</font>; | |||
# use a variable to store the upstream proxy | |||
# in this example we are using a hostname which is resolved via DNS | |||
# (if you aren't using DNS remove the resolver line and change the variable to point to an IP address e.g `set $jellyfin 127.0.0.1`) | |||
set $jellyfin <font color = blue>192.123.456.789</font>; | |||
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/<font color = blue>jellyfin.exemple.net</font>/fullchain.pem; | |||
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/<font color = blue>jellyfin.exemple.net</font>/privkey.pem; | |||
include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf; | |||
ssl_dhparam /etc/letsencrypt/ssl-dhparams.pem; | |||
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000" always; | |||
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/<font color = blue>jellyfin.exemple.net</font>/chain.pem; | |||
ssl_stapling on; | |||
ssl_stapling_verify on; | |||
# Security / XSS Mitigation Headers | |||
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN"; | |||
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block"; | |||
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff"; | |||
# Content Security Policy | |||
# See: <nowiki>https://</nowiki>developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CSP | |||
# Enforces https content and restricts JS/CSS to origin | |||
# External Javascript (such as cast_sender.js for Chromecast) must be whitelisted. | |||
add_header Content-Security-Policy "default-src https: data: blob:; style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline'; script-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' <nowiki>https://</nowiki>www.gstatic.com/cv/js/sender/v1/cast_sender.js; worker-src 'self' blob:; connect-src 'self'; object-src 'none'; frame-ancestors 'self'"; | |||
location / { | |||
# Proxy main Jellyfin traffic | |||
proxy_pass <nowiki>http://</nowiki>$jellyfin:8096; | |||
##proxy_pass <nowiki>https://</nowiki>$jellyfin:8920; | |||
proxy_set_header Host $host; | |||
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; | |||
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; | |||
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; | |||
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Protocol $scheme; | |||
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $http_host; | |||
# Disable buffering when the nginx proxy gets very resource heavy upon streaming | |||
proxy_buffering off; | |||
} | |||
# location block for /web - This is purely for aesthetics so /web/#!/ works instead of having to go to /web/index.html/#!/ | |||
## location ~ ^/web/ { | |||
## # Proxy main Jellyfin traffic | |||
## proxy_pass <nowiki>http://</nowiki>$jellyfin:8096/web/index.html; | |||
## ##proxy_pass <nowiki>https://</nowiki>$jellyfin:8920/web/index.html/$1; | |||
## proxy_set_header Host $host; | |||
## proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; | |||
## proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; | |||
## proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; | |||
## proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Protocol $scheme; | |||
## proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $http_host; | |||
## } | |||
location /socket { | |||
# Proxy Jellyfin Websockets traffic | |||
proxy_pass <nowiki>http://</nowiki>$jellyfin:8096; | |||
##proxy_pass <nowiki>https://</nowiki>$jellyfin:8920; | |||
proxy_http_version 1.1; | |||
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; | |||
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade"; | |||
proxy_set_header Host $host; | |||
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; | |||
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; | |||
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; | |||
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Protocol $scheme; | |||
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $http_host; | |||
} | |||
} | |||
== Migration de serveur == | |||
[https://jellyfin.org/docs/general/administration/migrate.html Source] | |||
{{Méta bandeau | |||
| niveau = information | |||
| icône = loupe | |||
| texte = Exemple testé de Debian 11 (VM) a Debian 11 (LXC) | |||
}} | |||
Références : | |||
JELLYFIN_CACHE_DIR=/var/cache/jellyfin | |||
JELLYFIN_CONFIG_DIR=/etc/jellyfin | |||
JELLYFIN_DATA_DIR=/var/lib/jellyfin | |||
JELLYFIN_LOG_DIR=/var/log/jellyfin | |||
<font color = blue>192.123.456.789</font> | |||
On coupe Jellyfin sur le serveur cible : | |||
srvdest# service jellyfin stop | |||
Si nécessaire on active l'accès SSH pour l'utilisateur root sur le serveur cible le temps du transfert : | |||
srvdest# vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config | |||
<font color = grey>... | |||
#LoginGraceTime 2m | |||
<font color = blue>PermitRootLogin yes</font> | |||
#StrictModes yes | |||
...</font> | |||
srvdest# service sshd restart | |||
On installe rsync transférer les fichiers en préservant les attributs : | |||
srvdest# apt install rsync | |||
Sur le serveur source on installe également rsync pour transférer les fichiers en préservant les attributs : | |||
srvsrc# apt install rsync | |||
On passe aux transferts.. : | |||
srvsrc# rsync -avP /var/cache/jellyfin/ <font color = blue>192.123.456.789</font>:/var/cache/jellyfin/ | |||
srvsrc# rsync -avP /etc/jellyfin/ <font color = blue>192.123.456.789</font>:/etc/jellyfin/ | |||
srvsrc# rsync -avP /var/lib/jellyfin/ <font color = blue>192.123.456.789</font>:/var/lib/jellyfin/ | |||
srvsrc# rsync -avP /var/log/jellyfin/ <font color = blue>192.123.456.789</font>:/var/log/jellyfin/ | |||
{{Méta bandeau | |||
| niveau = information | |||
| icône = loupe | |||
| texte = Remplacer <font color = blue>192.123.456.789</font> par l'adresse IP du serveur cible. | |||
}} | |||
Version actuelle datée du 21 mai 2024 à 19:58
LXC Debian 11
Installation
# apt update && apt upgrade # apt install apt-transport-https gnupg lsb-release # wget -O - https://repo.jellyfin.org/debian/jellyfin_team.gpg.key | apt-key add - # echo "deb [arch=$( dpkg --print-architecture )] https://repo.jellyfin.org/debian $( lsb_release -c -s ) main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jellyfin.list # apt update # apt install jellyfin
On peut sur rendre sur http://IP_SERVEUR:8096 pour vérifier le fonctionnement du service et faire la première configuration.
- On commence par le choix du langage préféré :
- On configure le compte d'administration et son mot de passe :
- On peut optionnelement inscrire tout de suite une ou plusieurs bibliothèques :
- Si l'on choisit d'ajouter une bibliothèque, on commence par choisir le type de médias et le nom, puis on choisit de configurer son emplacement :
- On indique le chemin d'accès du dossier et on valide :
- Une fois la/les bibliothèques configurées ou laissées pour plus tard on pass à l'étape suivante :
- Choix du langage par défaut pour les métadonnées :
- On configure l'accès distant (a priori par défaut) :
- Le serveur nous indique que la configuration de base est terminé :
- On est redirigé sur l'écran d'accueil :
Sécurisation de jellyfin
On crée le certificat :
# openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout /etc/jellyfin/jellyfin.key -out /etc/jellyfin/jellyfin.crt -nodes -subj '/CN=localhost' # openssl pkcs12 -export -inkey /etc/jellyfin/jellyfin.key -in /etc/jellyfin/jellyfin.crt -out /etc/jellyfin/jellyfin.pfx -passout pass: # chown jellyfin /etc/jellyfin/jellyfin.pfx
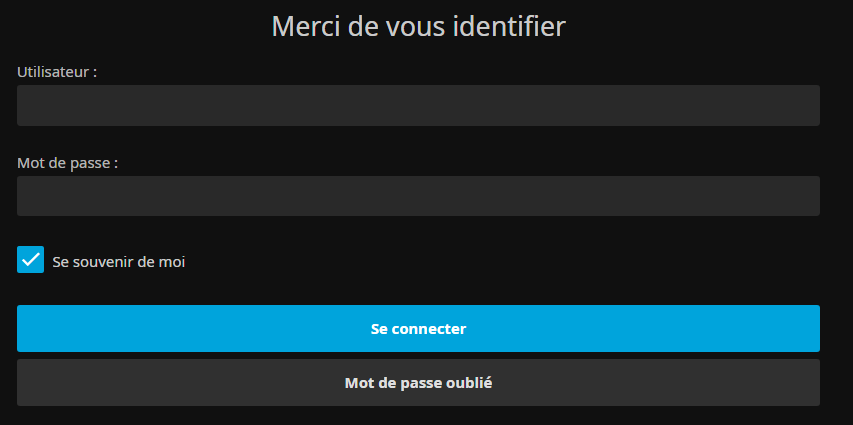
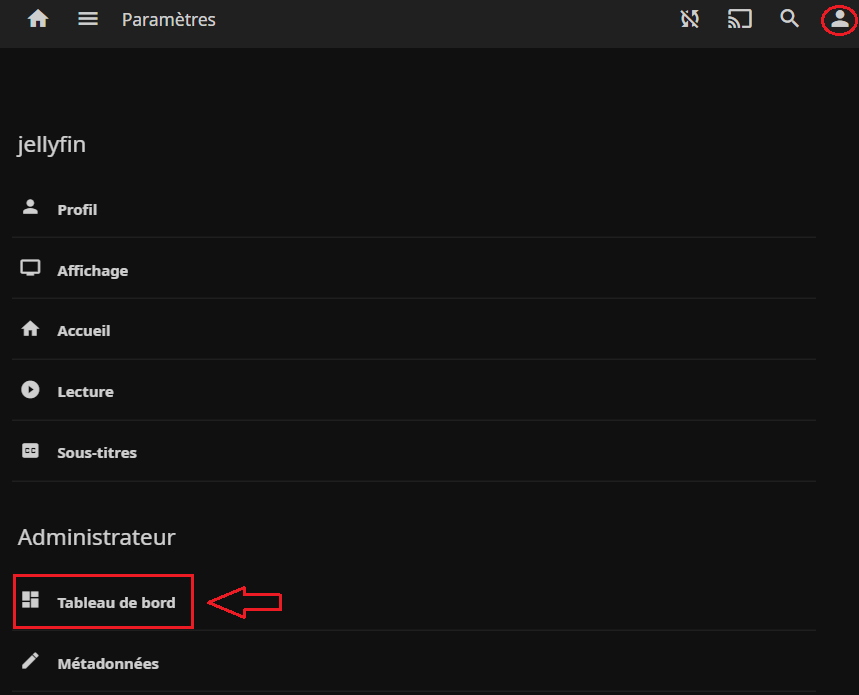
Puis on se connecte avec le compte "jellyfin" (administrateur) sur http://IP_SERVEUR:8096 et on se rend dans le tableau de bord :
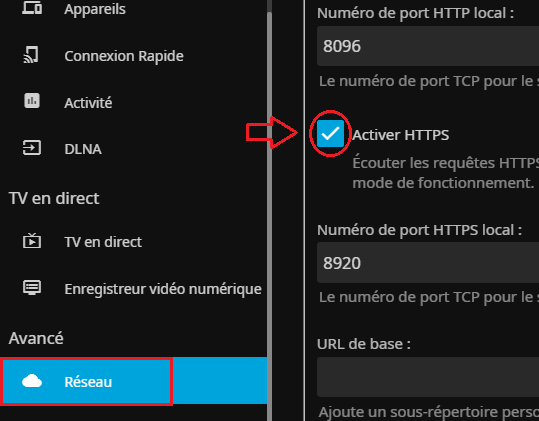
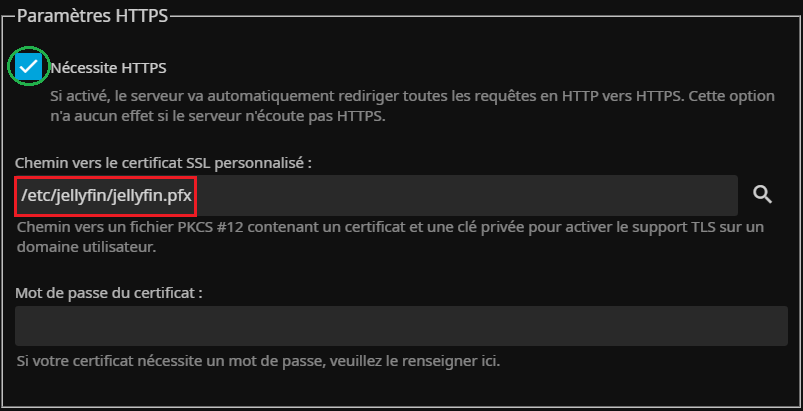
Dans le menu "Réseau" on active le HTTPS :
On peut forcer le HTTPS et on renseigne l'emplacement du certificat :
Enfin, on sauvegarde les modifications :
On redémarre le service :
# service jellyfin restart
Maintenant l'interface de Jellyfin sera accéssible via https://IP_SERVEUR:8920
Vhost pour Reverse-Proxy
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name jellyfin.exemple.net;
# Uncomment to redirect HTTP to HTTPS
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name jellyfin.exemple.net;
# use a variable to store the upstream proxy
# in this example we are using a hostname which is resolved via DNS
# (if you aren't using DNS remove the resolver line and change the variable to point to an IP address e.g `set $jellyfin 127.0.0.1`)
set $jellyfin 192.123.456.789;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/jellyfin.exemple.net/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/jellyfin.exemple.net/privkey.pem;
include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf;
ssl_dhparam /etc/letsencrypt/ssl-dhparams.pem;
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000" always;
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/jellyfin.exemple.net/chain.pem;
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
# Security / XSS Mitigation Headers
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN";
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block";
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff";
# Content Security Policy
# See: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CSP
# Enforces https content and restricts JS/CSS to origin
# External Javascript (such as cast_sender.js for Chromecast) must be whitelisted.
add_header Content-Security-Policy "default-src https: data: blob:; style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline'; script-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' https://www.gstatic.com/cv/js/sender/v1/cast_sender.js; worker-src 'self' blob:; connect-src 'self'; object-src 'none'; frame-ancestors 'self'";
location / {
# Proxy main Jellyfin traffic
proxy_pass http://$jellyfin:8096;
##proxy_pass https://$jellyfin:8920;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Protocol $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $http_host;
# Disable buffering when the nginx proxy gets very resource heavy upon streaming
proxy_buffering off;
}
# location block for /web - This is purely for aesthetics so /web/#!/ works instead of having to go to /web/index.html/#!/
## location ~ ^/web/ {
## # Proxy main Jellyfin traffic
## proxy_pass http://$jellyfin:8096/web/index.html;
## ##proxy_pass https://$jellyfin:8920/web/index.html/$1;
## proxy_set_header Host $host;
## proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
## proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
## proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
## proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Protocol $scheme;
## proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $http_host;
## }
location /socket {
# Proxy Jellyfin Websockets traffic
proxy_pass http://$jellyfin:8096;
##proxy_pass https://$jellyfin:8920;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Protocol $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $http_host;
}
}
Migration de serveur
Références : JELLYFIN_CACHE_DIR=/var/cache/jellyfin JELLYFIN_CONFIG_DIR=/etc/jellyfin JELLYFIN_DATA_DIR=/var/lib/jellyfin JELLYFIN_LOG_DIR=/var/log/jellyfin
192.123.456.789 On coupe Jellyfin sur le serveur cible :
srvdest# service jellyfin stop
Si nécessaire on active l'accès SSH pour l'utilisateur root sur le serveur cible le temps du transfert :
srvdest# vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
... #LoginGraceTime 2m PermitRootLogin yes #StrictModes yes ...
srvdest# service sshd restart
On installe rsync transférer les fichiers en préservant les attributs :
srvdest# apt install rsync
Sur le serveur source on installe également rsync pour transférer les fichiers en préservant les attributs :
srvsrc# apt install rsync
On passe aux transferts.. :
srvsrc# rsync -avP /var/cache/jellyfin/ 192.123.456.789:/var/cache/jellyfin/ srvsrc# rsync -avP /etc/jellyfin/ 192.123.456.789:/etc/jellyfin/ srvsrc# rsync -avP /var/lib/jellyfin/ 192.123.456.789:/var/lib/jellyfin/ srvsrc# rsync -avP /var/log/jellyfin/ 192.123.456.789:/var/log/jellyfin/